Click here in order to find our follow-up study from September 2016.
Since the end of February Facebook users have the possibility to express their feelings in other ways than just with a Like. This Facebook Reaction study analyzes 130,000 posts and reveals first findings on how Facebook users interact after the official launch. Facebook Reactions added five new options on how people are able to interact with content. For marketers, this feature offers some great information to analyze their content, conversations and community.
Through Facebook Reactions brands can get a deeper understanding on how content is perceived by their community. Information that can be gathered now make Sentiment Analysis (if your content is perceived positively or negatively) easier to measure. Until now this was not an easy task as irony or sarcasm were hardly measurable. Facebook Reactions analysis enable businesses to identify this at a glance.
On average Facebook Reactions have low significance
Taking a look at the share of interactions it is clear that 97% are likes, comments and shares.In this first step of our Facebook Reactions analysis it is clear that Facebook Reactions are not used very frequently by the average at this point. In our study, we also broke this share further down and looked at this split excluding shares and comments, which also revealed similar findings.
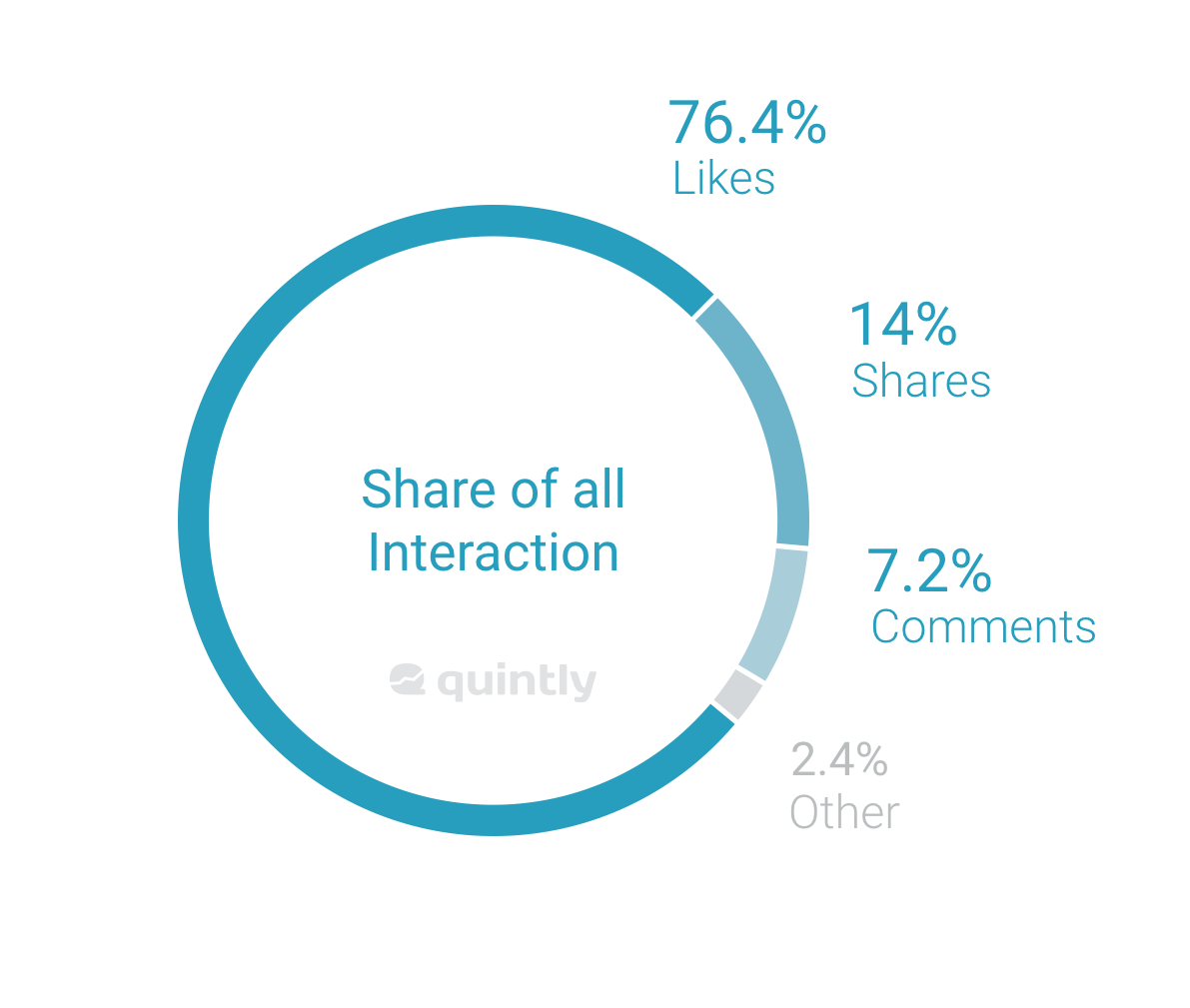
For marketers it would be highly beneficial to know how content is perceived in detail. Based on that, marketers would be able to adjust future content and improve their storytelling approach further. At this point, Facebook Reactions just need to establish or marketers need to post not only likeable but also “reactionable” content. Among the new options “Love” is predominantly used, even though users knew positive reactions already since the launch of Facebook through the Like button. From a marketer's point of view, the question to be answered at this stage is if Reactions will establish in the short run or if the content posted needs to change to receive a higher amount of reactions. Without a doubt, the information that could be gathered could be a game-changer for marketing.
Videos receive 40% more Reactions than image posts
To give marketers an approach to receive more reactions and in the end more information about their community, posting more video content could be part of the solution. In the analyzed 130,000 posts we found that videos receive more reactions (love, wow, haha, sad, angry). This analysis shows that video content can generate more emotions, positive as well as negative. Especially after consuming videos users tend to react with a “wow” reaction significantly more often compared to images. Same applies for the “angry” reaction which users are twice as likely to interact with after watching a video. The findings reveal that video content is able to stir emotions more than images. The like count for the average image was in contrast higher; thus people seem to express their feelings quicker using the like function.
Another takeaway of our Facebook Reaction Study is that users interacted with the analyzed posts mainly positive. This finding can be seen in the table above where you see a clear difference between all positive and negative expressions of feeling. Until the launch of Facebook Reactions it was hardly possible to express a negative perception. Now it is, but the share of people using it is very low. While Facebook timelines do contain not only happy and entertaining content but also bad news and controversial statements of politics or similar. That shows, Facebook users prefer to interact with content that entertains, is funny or just generates positive emotions.
For marketers sharing the stories on Facebook it is essential to start measuring the Facebook Reaction effectiveness to adjust future content.
